pornographer n.
1847, "
Entries linking to pornographer
1842, "
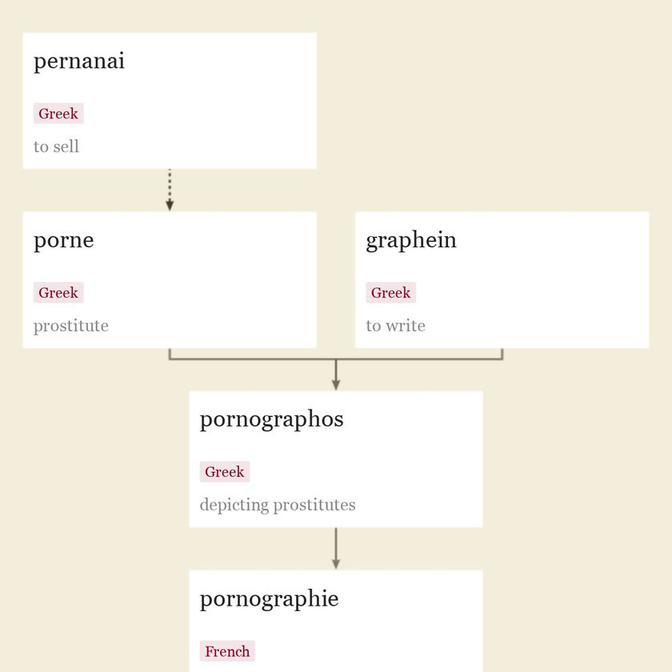
A brothel in ancient Greek was a porneion. In reference to modern works by 1859 (originally French novels), later as a charge against native literature; the sense of "
Pornography, or obscene painting, which in the time of the Romans was practiced with the grossest license, prevailed especially at no particular period in Greece, but was apparently tolerated to a considerable extent at all times. Parrhasius, Aristides, Pausanias, Nicophanes, Chaerephanes, Arellius, and a few other [pornographoi] are mentioned as having made themselves notorious for this species of license. [Charles Anthon, "Dictionary of Greek and Roman Antiquities," New York, 1843]
I shall not today attempt further to define the kinds of material I understand to be embraced within that shorthand description [hard-core pornography]; and perhaps I could never succeed in intelligibly doing so. But I know it when I see it, and the motion picture involved in this case is not that. [U.S. Supreme Court Justice Potter Stewart, concurring opinion, "Jacobellis v. Ohio," 1964]
E. Bray in The Medical Archives [December 1872] proposed porniatria for "
Pornocracy (1860) is "
English agent noun ending, corresponding to Latin -or. In native words it represents Old English -ere (Old Northumbrian also -are) "
Generally used with native Germanic words. In words of Latin origin, verbs derived from past participle stems of Latin ones (including most verbs in -ate) usually take the Latin ending -or, as do Latin verbs that passed through French (such as governor); but there are many exceptions (eraser, laborer, promoter, deserter; sailor, bachelor), some of which were conformed from Latin to English in late Middle English.
The use of -or and -ee in legal language (such as lessor/lessee) to distinguish actors and recipients of action has given the -or ending a tinge of professionalism, and this makes it useful in doubling words that have a professional and a non-professional sense (such as advisor/adviser, conductor/conducter, incubator/incubater, elevator/elevater).
updated on September 04, 2020