father-in-law n.
late 14c., from father (n.) + in-law.
Entries linking to father-in-law
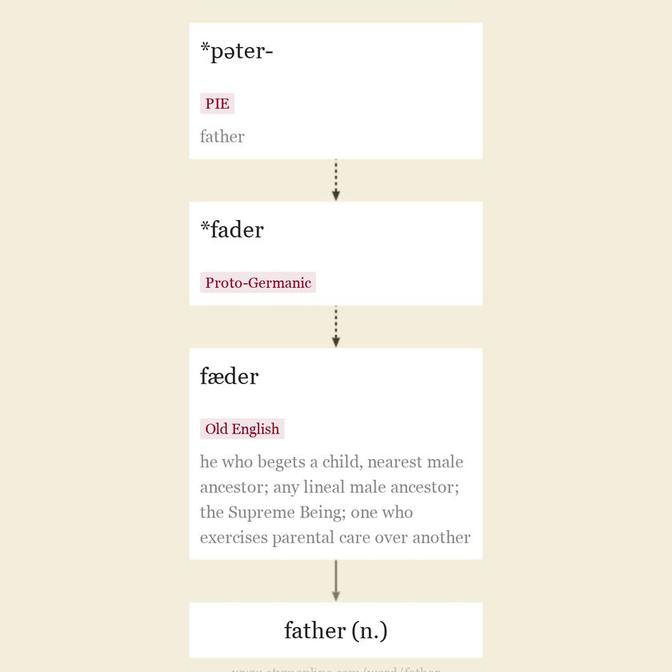
Old English fæder "
My heart leaps up when I behold
A rainbow in the sky:
So was it when my life began;
So is it now I am a man;
So be it when I shall grow old,
Or let me die!
The Child is father of the Man;
I could wish my days to be
Bound each to each by natural piety.
[Wordsworth, 1802]
The classic example of Grimm's Law, where PIE "
1894, "
The position of the 'in-laws' (a happy phrase which is attributed ... to her Majesty, than whom no one can be better acquainted with the article) is often not very apt to promote happiness. [Blackwood's Magazine, 1894]
The earliest recorded use of the formation is in brother-in-law (13c.); the law is Canon Law, which defines degrees of relationship within which marriage is prohibited. Thus the word originally had a more narrow application; its general extension to more distant relatives of one's spouse is, according to OED "
updated on October 10, 2017