| 词源 |
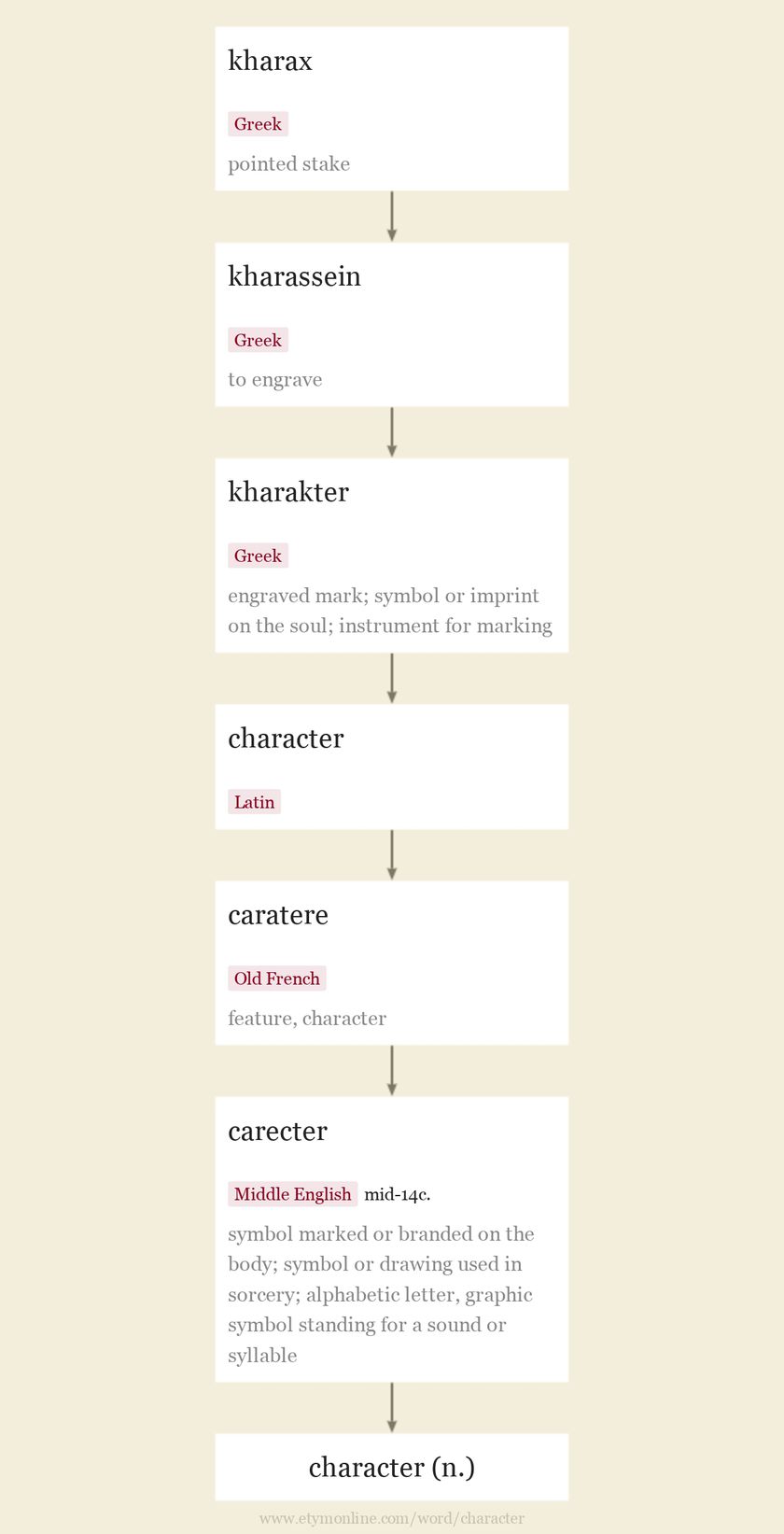
character n.mid-14c., carecter, "symbol marked or branded on the body;" mid-15c., "symbol or drawing used in sorcery;" late 15c., "alphabetic letter, graphic symbol standing for a sound or syllable;" from Old French caratere "feature, character" (13c., Modern French caractère), from Latin character, from Greek kharaktēr "engraved mark," also "symbol or imprint on the soul," properly "instrument for marking," from kharassein "to engrave," from kharax "pointed stake," a word of uncertain etymology which Beekes considers "most probably Pre-Greek." In English the Latin ch- spelling was restored from 1500s. The meaning of Greek kharaktēr was extended in Hellenistic times by metaphor to "a defining quality, individual feature." In English, the meaning "sum of qualities that define a person or thing and distinguish it from another" is from 1640s. That of "moral qualities assigned to a person by repute" is from 1712. You remember Eponina, who kept her husband alive in an underground cavern so devotedly and heroically? The force of character she showed in keeping up his spirits would have been used to hide a lover from her husband if they had been living quietly in Rome. Strong characters need strong nourishment. [Stendhal "de l'Amour," 1822] The sense of "person in a play or novel" is first attested 1660s, in reference to the "defining qualities" he or she is given by the author. The meaning "a person" in the abstract is from 1749; especially "eccentric person" (1773). The colloquial sense of "chap, fellow" is from 1931. Character-actor, one who specializes in characters with marked peculiarities, is attested from 1861; character assassination is so called from 1888; character building (n.) from 1886. updated on November 25, 2022 |