believable adj.
"
Entries linking to believable
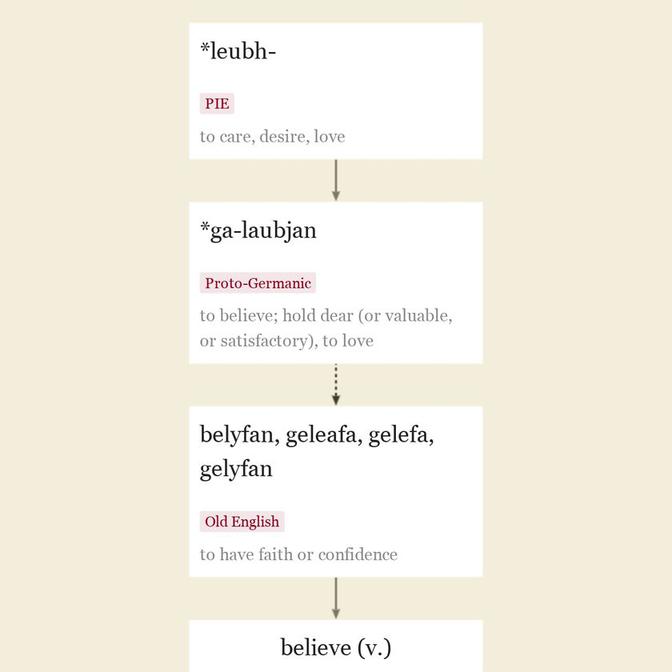
Middle English bileven, from Old English belyfan "
The meaning "
The form beleeve was common till 17c., the spelling then changed, perhaps by influence of relieve, etc. To believe on instead of in was more common in 16c. but now is a peculiarity of theology; believe of also sometimes was used in 17c. The expression believe it or not is attested by 1874; Robert Ripley's newspaper cartoon of the same name is from 1918. Emphatic you better believe attested from 1854.
common termination and word-forming element of English adjectives (typically based on verbs) and generally adding a notion of "
A living element in English, used in new formations from either Latin or native words (readable, bearable) and also with nouns (objectionable, peaceable). Sometimes with an active signification (suitable, capable), sometimes of neutral signification (durable, conformable). It has become very elastic in meaning, as in a reliable witness, a playable foul ball, perishable goods. A 17c. writer has cadaverable "
To take a single example in detail, no-one but a competent philologist can tell whether reasonable comes from the verb or the noun reason, nor whether its original sense was that can be reasoned out, or that can reason, or that can be reasoned with, or that has reason, or that listens to reason, or that is consistent with reason; the ordinary man knows only that it can now mean any of these, & justifiably bases on these & similar facts a generous view of the termination's capabilities; credible meaning for him worthy of credence, why should not reliable & dependable mean worthy of reliance & dependence? [Fowler]
In Latin, -abilis and -ibilis depended on the inflectional vowel of the verb. Hence the variant form -ible in Old French, Spanish, English. In English, -able tends to be used with native (and other non-Latin) words, -ible with words of obvious Latin origin (but there are exceptions). The Latin suffix is not etymologically connected with able, but it long has been popularly associated with it, and this probably has contributed to its vigor as a living suffix.
updated on October 06, 2022