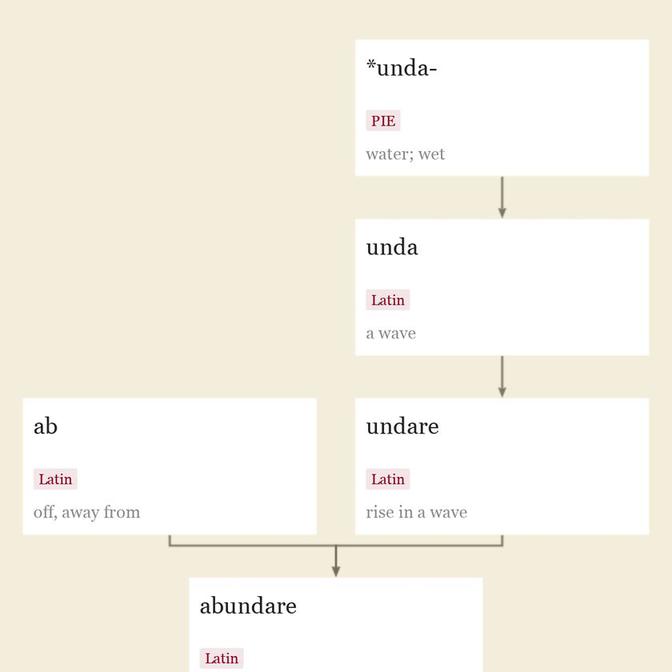
superabundance n.
early 15c., superaboundance, from Late Latin superabundantia, from present participle stem of Latin superabundare, from super (see super-) + abundare (see abound). Related: Superabundant; superabound.
updated on December 28, 2013
- psycho
- psychoactive
- psychoanalysis
- psychoanalyst
- psychoanalytic
- psychoanalyze
- psychobabble
- psychodectic
- psychodrama
- psychodynamic
- psychogenesis
- psychogenic
- psychographic
- psychography
- psychohistory
- psychokinesis
- psychological
- psychologist
- psychologize
- psychology
- psychomancy
- psychometrics
- psychometry
- psychomotor
- psychopath